Intracranial pressure (ICP): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
= | = ICP monitoring = | ||
== Purpose of ICP monitoring == | |||
# Early warning | |||
# Goal directed Tx | |||
== Indications (BTF) == | |||
# abnml CT | # abnml CT | ||
# GCS <9 | # GCS <9 | ||
# Hx of TBI | # Hx of TBI | ||
[[Category:Neurophysiology]] | [[Category:Neurophysiology]] | ||
[[Category:Neurotrauma]] | [[Category:Neurotrauma]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:26, 22 November 2024
- Normal ICP: <10-15 mmHg, varies w/ age, position, straining, & coughing
ICP & intracranial volume
- Brain parenchyma: 1400 ml (80% total, 10% solid, 70% tissue water)
- CBV: 150 ml (10% total)
- CSF: 150 ml (10% total) (tot. ~1700 ml)
Monro-Kellie doctrine
- ↑ in vol. of one intracranial compartment → ↑ ICP unless offset by ↓ vol. in another compartment
- Brain parenchyma predominantly incompressible fluid, CBV & CSF key in buffering additional intracranial volume by ↑ venous outflow/↓ CBF, displacing/↓ intracranial CSF
- Infants have extra volume compensation w/ open fontanelle
- Pathologic processes can easily ↑ ICP by exceeding compensatory capacity due to small size of CBV & CSF compartments
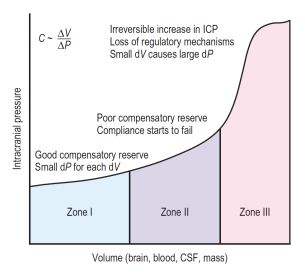
Pressure-Volume curve
- Additional intracranial volume initially accommodated w/ little/no Δ ICP (flat part of curve)
- Once craniospinal buffering capacity exhausted (decompensation point), small ↑ in intracranial vol. → substantial ↑ ICP
Davson equation
ICP = If * Rout - PSS
- resistance to cerebrospinal fluid outflow (Rout)
- formation of cerebrospinal fluid (If)
- sagittal sinus pressure (PSS)
ICP monitoring
Purpose of ICP monitoring
- Early warning
- Goal directed Tx
Indications (BTF)
- abnml CT
- GCS <9
- Hx of TBI