Maxillary Artery: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Maxillary Artery .png|thumb|Left lateral view. The maxillary artery is the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery. Its origin lies deep to the mandibular ramus (important landmark for locating the vessel). The maxillary artery consists of three parts: | [[File:Maxillary Artery .png|thumb|Left lateral view. The maxillary artery is the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery. Its origin lies deep to the mandibular ramus (important landmark for locating the vessel). The maxillary artery consists of three parts: <ul><li>Mandibular part (blue) </li> <li>Pterygoid part (green) </li> <li>Pterygopalatine part (yellow)</li></ul>]] | ||
]] | |||
* Arises as a terminal branch of the [[External Carotid Artery|external carotid artery]] w/ the superficial temporal artery | * Arises as a terminal branch of the [[External Carotid Artery|external carotid artery]] w/ the superficial temporal artery | ||
* passes through infratemporal fossa → (via pterygomaxillary fissure) pterygopalatine fossa. follow the maxillary nerve. | * passes through infratemporal fossa → (via pterygomaxillary fissure) pterygopalatine fossa. follow the maxillary nerve. | ||
Latest revision as of 05:07, 3 August 2024
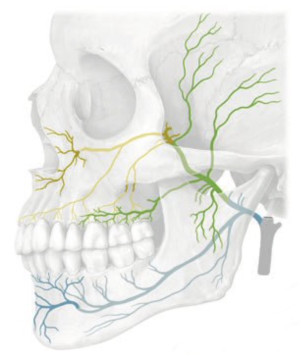
- Mandibular part (blue)
- Pterygoid part (green)
- Pterygopalatine part (yellow)
- Arises as a terminal branch of the external carotid artery w/ the superficial temporal artery
- passes through infratemporal fossa → (via pterygomaxillary fissure) pterygopalatine fossa. follow the maxillary nerve.
Segments
- Divided into three segments:
- Second segment - courses in an anterior, medial & superior direction; gives rise to:
- infraorbital artery → passes through the inferior orbital fissure & courses w/ the infraorbital nerve;
- anastomoses w/ ophthalmic artery (OA)
- posterosuperior alveolar artery → descends to pierce the posterolateral wall of the maxilla;
- recurrent meningeal branches → pass through the foramen rotundum
- infraorbital artery → passes through the inferior orbital fissure & courses w/ the infraorbital nerve;
- pterygopalatine segment (third) in the pterygopalatine fossa → divides into its terminal branches:
- the greater and lesser palatine arteries. which descend through the greater and lesser palatine canals;
- the vidian artery to the pterygoid canal;
- the pharyngeal branch to the palatovaginal canal;
- sphenopalatine artery → sphenopalatine foramen to reach the nasal cavity (considered to be the terminal branch, because of its large diameter)
- Second segment - courses in an anterior, medial & superior direction; gives rise to:
Branches and distribution
Mandibular part
- Inferior alveolar artery ⇒ Mandible, teeth, gingiva (the mental branch is its terminal branch)
- Middle meningeal artery ⇒ Calvaria, dura, anterior and middle cranial fossae
- Deep auricular artery ⇒ Temporomandibular joint, external auditory canal
- Anterior tympanic artery ⇒ Tympanic cavity
Pterygoid part
- Masseteric artery ⇒ Masseter muscle
- Deep temporal branches ⇒ Temporalis muscle
- Pterygoid branches ⇒ Pterygoid muscles
- Buccal artery ⇒ Buccal mucosa
Pterygopalatine part
- Posterior superior alveolar artery ⇒ Maxillary molars, maxillary sinus, gingiva
- Infraorbital artery ⇒ Maxillary alveoli
- Descending palatine artery:
- Greater palatine artery ⇒ Hard palate
- Lesser palatine artery ⇒ Soft palate, palatine tonsil, pharyngeal wall
- Sphenopalatine artery:
- Lateral posterior nasal arteries ⇒ Lateral wall of the nasal cavity, conchae
- Posterior septal branches ⇒ Nasal septum