Meningioma: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
[[File:Meningioma - Histopathology .jpg|thumb|500x500px]] | [[File:Meningioma - Histopathology .jpg|thumb|500x500px]] | ||
* The tumour cells have features of both syncytial and fibroblastic type forming <mark>whorls</mark> which contain central laminated areas of calcification called <mark>psammoma bodies</mark>. | * The tumour cells have features of both syncytial and fibroblastic type forming <mark>whorls</mark> which contain central laminated areas of calcification called <mark>psammoma bodies</mark>. | ||
<br clear="all"> | |||
== Immunohistochemical staining == | == Immunohistochemical staining == | ||
Revision as of 22:46, 4 March 2024
Related pages
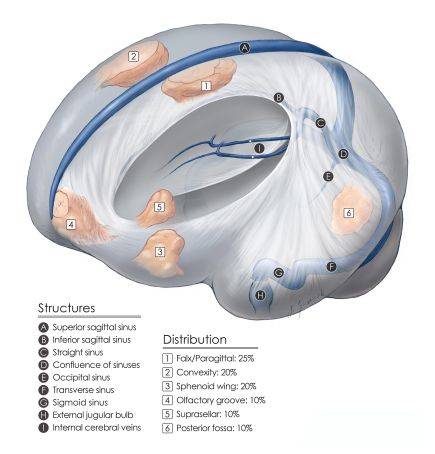
General information
- Meningiomas are a group of tumors that are believed to originate in meningothelial cells of the arachnoid membrane.
- They may be intracranial (MC), intraorbital, or intra-spinal.
Meningioma Grades
| GRADE I | GRADE II | GRADE III |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Diagnosis
Imaging findings
- Wide dural based
- Hyperostosis
- Dural tail
- Calcifications
- Homogeneous enhancement
- Pneumosinus dilatans
- MRI: isointense on T1WI, hypointense on T2WI
Histopathology
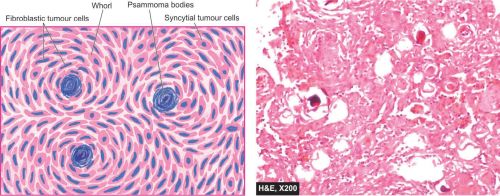
- The tumour cells have features of both syncytial and fibroblastic type forming whorls which contain central laminated areas of calcification called psammoma bodies.
Immunohistochemical staining
- EMA ⊕ in ~80%