Neural Control of Micturition: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* Activation of S2-S4 α-motor neurons causing contraction of the external urethral sphincter striated muscle fibers | * Activation of S2-S4 α-motor neurons causing contraction of the external urethral sphincter striated muscle fibers | ||
** Allows for the voluntary retention of urine once a full bladder has induced an increase in bladder parasympathetic tone | ** Allows for the voluntary retention of urine once a full bladder has induced an increase in bladder parasympathetic tone | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Neural Control of Micturition.jpg|alt= | File:Index.php?title=File:Neural Control of Micturition.jpg|alt= | ||
File:Autonomic and somatic innervation of the lower urinary tract.jpg|Autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) and somatic innervation of the lower urinary tract. ''ACh,'' Acetylcholine. | File:Index.php?title=File:Autonomic and somatic innervation of the lower urinary tract.jpg|Autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) and somatic innervation of the lower urinary tract. ''ACh,'' Acetylcholine. | ||
File:Parasympathetic innervation of the bladder.jpg|Parasympathetic innervation of the bladder. | File:Index.php?title=File:Parasympathetic innervation of the bladder.jpg|Parasympathetic innervation of the bladder. | ||
File:Sympathetic innervation of the bladder.jpg|Sympathetic innervation of the bladder. | File:Index.php?title=File:Sympathetic innervation of the bladder.jpg|Sympathetic innervation of the bladder. | ||
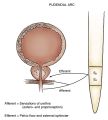
File:Pudendal innervation of the urethra and pelvic floor..jpg|Pudendal innervation of the urethra and pelvic floor. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[Category:Neurophysiology]] | |||
Revision as of 05:02, 23 March 2024
- A full bladder sends afferent signals causing inhibition of sympathetic tone and an increase in parasympathetic activity to the bladder through the pelvic splanchnic nerves.
- The parasympathetic activity relaxes the internal urethral sphincter and induces bladder contraction.
- The external urethral sphincter is under voluntary (somatic) control, and muscle fiber contraction causes closure of the sphincter.
- Activation of S2-S4 α-motor neurons causing contraction of the external urethral sphincter striated muscle fibers
- Allows for the voluntary retention of urine once a full bladder has induced an increase in bladder parasympathetic tone
-
-
Autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) and somatic innervation of the lower urinary tract. ACh, Acetylcholine.
-
Parasympathetic innervation of the bladder.
-
Sympathetic innervation of the bladder.
-
Pudendal innervation of the urethra and pelvic floor.