Carpal Tunnel: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[File:Carpal tunnel.png|thumb|252x252px]] | [[File:Carpal tunnel.png|thumb|252x252px]] | ||
== Pressure within carpal tunnel == | |||
{ class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Pressure (mm Hg) | |||
| <20 | normal | | !Description | ||
| 20-30 | venular flow retarded | | |- | ||
| 30 | axonal transport impaired | | |<20 | ||
| 40 | sensory & motor dysfunction | | |normal | ||
| 60-80 | blood flow ceases |} | |- | ||
|20-30 | |||
|venular flow retarded | |||
|- | |||
|30 | |||
|axonal transport impaired | |||
|- | |||
|40 | |||
|sensory & motor dysfunction | |||
|- | |||
|60-80 | |||
|blood flow ceases | |||
|} | |||
Revision as of 11:25, 13 September 2023
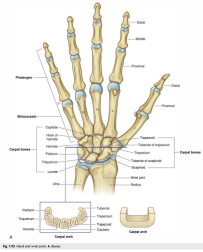
Boundaries of the Carpal Tunnel
- Roof: Flexor retinaculum.
- Floor: Carpal bones (hamate, capitate, trapezoid, trapezium, pisiform, triquetrum, lunate, and scaphoid).
- Medial Boundary: Pisiform and hamate bones.
- Lateral Boundary: Scaphoid and trapezium bones.
Attachments of the Flexor retinaculum
- Medially: It attaches to the pisiform and the hook of the hamate.
- Laterally: It attaches to the scaphoid tubercle and the trapezium.
Pressure within carpal tunnel
| Pressure (mm Hg) | Description |
|---|---|
| <20 | normal |
| 20-30 | venular flow retarded |
| 30 | axonal transport impaired |
| 40 | sensory & motor dysfunction |
| 60-80 | blood flow ceases |