Craniosynostosis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
|HCP rare | |HCP rare | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |[[Apert Syndrome]] (acrocephalosyndactyly) <html><span style="background-color:#fff2cc;">(MC)</span></html> | ||
|Yes (95%) | |Yes (95%) | ||
|FGFR2 (AD) | |FGFR2 (AD) | ||
Revision as of 14:36, 3 February 2024
Types of craniosynostosis
Nonsyndromic Craniosynostosis
Single suture craniosynostosis
Pathology
- Bone growth primarily perpendicular to & occurring at suture lines; premature fusion → abnormal growth
Classification of single suture craniosynostosis
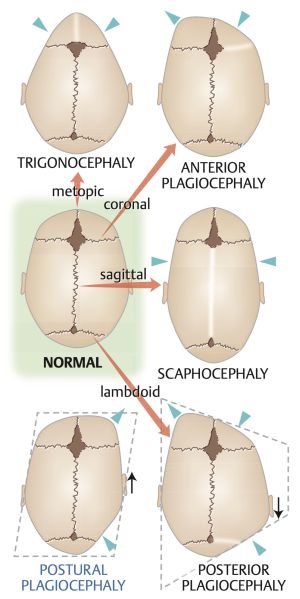
Syndromic craniosynostosis
Selected craniofacial dysmorphic syndromes
| Syndrome | Sporadic | Inherited | Craniofacial findings | Associated findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crouzon Syndrome (craniofacial dysostosis) | Yes (25%) | FGFR2 (AD) | Craniosynostosis of coronal & basal skull sutures, maxillary hypoplasia, shallow orbits, proptosis | HCP rare |
| Apert Syndrome (acrocephalosyndactyly) (MC) | Yes (95%) | FGFR2 (AD) | same as Crouzon | Syndactyly of digits 2, 3, 4; shortened UE, HCP common |
| Kleeblattschädel Syndrome | Yes | AD | Craniosynostosis /w trilobular skull | isolated, or with Apert's or thanatophoric dwarfism |