Posterior Cerebral Artery: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
<td>Meningeal branches</td> | <td>Meningeal branches</td> | ||
<td>Supply: tentorium and the falx</td> | <td>Supply: tentorium and the falx</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== P2 segment == | |||
<table class="wikitable" width="100%"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th width="30%">P2 Segment</th> | |||
<th>Feature</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Lateral posterior choroidal artery</td> | |||
<td> | |||
* Main branch of P2, courses over the pulvinar and through the choroidal fissure | |||
* Supply: posterior portion of the thalamus and choroid plexus (temporal horn and atrium) | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Thalamogeniculate arteries</td> | |||
<td>Medial geniculate body, lateral geniculate body, pulvinar, superior colliculus, and crus cerebri</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Cortical branches</td> | |||
<td> | |||
* Inferior temporal artery group | |||
* Supply: inferior portion of the temporal lobe | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== P3 segment == | |||
<table class="wikitable" width="100%"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th width="30%">P3 Segment</th> | |||
<th>Feature</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Posterior temporal artery</td> | |||
<td> | |||
* Posterior temporal lobe, occipitotemporal and lingual gyri | |||
* Anterior temporal artery branch travels to the inferior temporal lobe to supply the inferior cortex. | |||
* Anastomoses with middle cerebral artery | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Internal occipital artery</td></tr><tr> | |||
<td>Parietooccipital artery</td> | |||
<td> | |||
* Located in the parietooccipital sulcus | |||
* Supply: posterior ⅓ of the medial hemispheres, cuneus, precuneus, superior occipital gyrus, and precentral and superior parietal lobules | |||
* Anastomoses with anterior cerebral artery | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Calcarine artery</td> | |||
<td> | |||
* Located in the calcarine sulcus | |||
* Supply: occipital pole and the visual cortex | |||
* Anastomoses with middle cerebral artery | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Posterior pericallosal artery</td> | |||
<td> | |||
* Supply: splenium of the corpus callosum | |||
* Anastomoses with anterior cerebral artery</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 3 March 2024
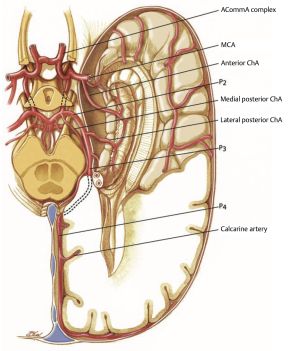
Anatomical segments
- P1: PCA from the origin to posterior communicating artery (AKA mesencephalic, precommunicating, circular, peduncular, basilar...). The long and short circumflex and thalamoperforating arteries arise from P1
- P2: PCA from origin of PComA to the origin of inferior temporal arteries (AKA ambient, post-communicating, perimesencephalic), P2 traverses the ambient cistern, hippocampal, anterior temporal, peduncular perforating, and medial posterior choroidal arteries arise from P2
- P3: PCA from the origin of the inferior temporal branches to the origin of the terminal branches (AKA quadrigeminal segment). P3 traverses the quadrigeminal cistern
- P4: segment after the origin of the parieto-occipital and calcarine arteries, includes the cortical branches of the PCA
P1 segment
| P1 Segment | Feature |
|---|---|
| Posterior thalamoperforator arteries |
|
| Medial posterior choroidal arteries |
|
| Meningeal branches | Supply: tentorium and the falx |
P2 segment
| P2 Segment | Feature |
|---|---|
| Lateral posterior choroidal artery |
|
| Thalamogeniculate arteries | Medial geniculate body, lateral geniculate body, pulvinar, superior colliculus, and crus cerebri |
| Cortical branches |
|
P3 segment
| P3 Segment | Feature |
|---|---|
| Posterior temporal artery |
|
| Internal occipital artery | |
| Parietooccipital artery |
|
| Calcarine artery |
|
| Posterior pericallosal artery |
|
Vascular territory
- parietooccipital sulcus (medial) and inferior temporal sulcus (lateral)