Meningioma: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Tag: Reverted |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Optic nerve/chiasm</td> | <td>Optic nerve/chiasm</td> | ||
<td>Inferolat</td> | <td>Inferolat → pushes backward</td> | ||
<td>Superolat</td> | <td>Superolat → pushes upward</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
Revision as of 19:22, 3 March 2024
Related pages
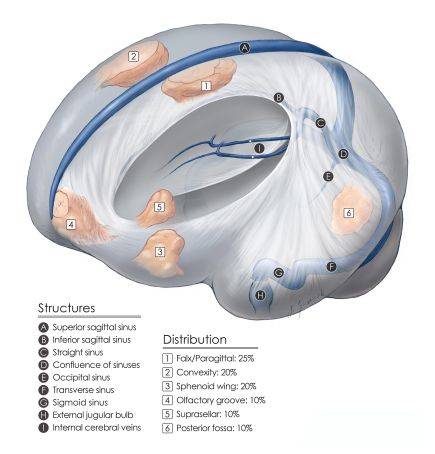
General information
- Meningiomas are a group of tumors that are believed to originate in meningothelial cells of the arachnoid membrane.
- They may be intracranial (MC), intraorbital, or intra-spinal.
Anterior skull base Meningiomas
Nomenclature
- Olfactory Groove Meningiomas (OGM)
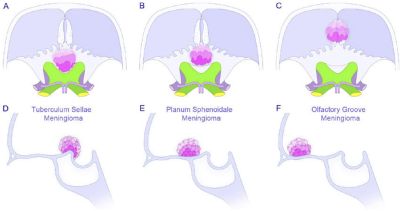
Nomenclature of anterior skull base meningiomas - Planum Sphenoidale Meningiomas
- Tuberculum Sellae Meningioma (TSM)
Clinical Presentation
- Personality Δ
- H/A
- Sz's
- Visual deficits
- Anosmia
- Foster-Kennedy syndrome of unilateral optic atrophy and contralateral papilledema
Comparison of OGM and TSM
| Factor | OGM | TSM |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Cribriform, frontosphenoid suture | Planum sphenoidale, tuberculum sellae |
| Blood supply | Ant & pos ethmoidals, middle meningeal, ophthalmic (meningeal branch, ACA & ACoA) | Pos ethmoidal (ACA & ACoA) |
| Olfactory nerves | Superolat | Inferolat |
| Optic nerve/chiasm | Inferolat → pushes backward | Superolat → pushes upward |
| ACA | Pos. to posterosuperior | Posterosuperior |
Diagnosis
Imaging findings
- Wide dural based
- Hyperostosis
- Dural tail
- Calcifications
- Homogeneous enhancement
- Pneumosinus dilatans
- MRI: isointense on T1WI, hypointense on T2WI