Medulloblastoma: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Pathology = | = Pathology = | ||
== Microscopic Appearance of Medulloblastoma == | == Microscopic Appearance of Medulloblastoma == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 14: | ||
= Subtypes = | = Subtypes = | ||
[[File:Medulloblastoma - subtypes.jpg|thumb|342x342px]] | |||
== Classic or undifferentiated medulloblastoma (A) == | == Classic or undifferentiated medulloblastoma (A) == | ||
* Highly cellular tumor | * Highly cellular tumor | ||
Revision as of 21:29, 3 March 2024
Pathology
Microscopic Appearance of Medulloblastoma
- Dense sheet of small, basophilic cells
- Little cytoplasm
- Round to oval hyperchromatic nuclei
- High mitotic index
- Evidence of neuronal or glial differentiation in up to 50% of cases
- Homer Wright rosettes are commonly present
Homer Wright Rosettes
- Homer Wright rosettes are a characteristic microscopic feature of medulloblastoma
- They are thought to represent abortive attempts at neuronal differentiation
- Homer Wright rosettes are not pathognomonic of medulloblastoma and can be seen in other tumors, such as ependymoma
Subtypes
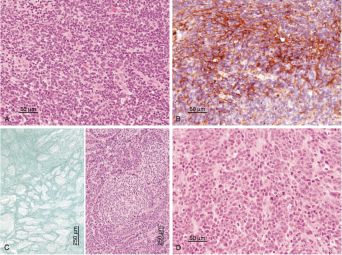
Classic or undifferentiated medulloblastoma (A)
- Highly cellular tumor
- Sheets of small oval or round blue cells
Classic medulloblastoma with area of glial fibrillary acidic protein immunopositivity (B)
- Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a marker of glial differentiation
- The presence of GFAP-positive cells in medulloblastoma suggests that the tumor may have a glial component
Desmoplastic medulloblastoma (C)
- Reticulin-positive internodular zones and reticulin-free pale islands
- Desmoplastic medulloblastoma is a rare subtype of medulloblastoma that is characterized by the presence of reticulin-positive internodular zones and reticulin-free pale islands
Large cell medulloblastoma (D)
- Increased nuclear size with abundant mitoses
- Large cell medulloblastoma is a rare subtype of medulloblastoma that is characterized by the presence of large cells with increased nuclear size and abundant mitoses