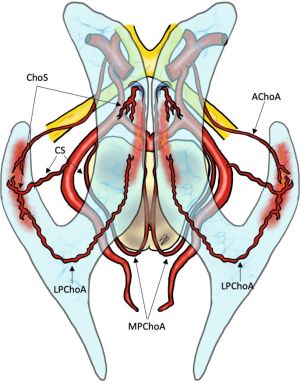
Choroidal arteries
Anterior Choroidal arteries
ant. choroidal a.: takeoff 2–4mm distal to PComA ⇒ (variable) portion of optic tract, medial GP, genu of IC (in 50%), inf. half of pos. limb of IC, uncus, retrolenticular fibers (optic radiation), LGBN;
AChA syndrome, triad: CL hemiplegia, hemihypesthesia & homonymous hemianopsia (mnemonic: 3 H’s); however, incomplete forms are MC; Occlusion is usually d/t small vessel dz → pos. limb of IC
- Arise from the ICA
- Course: goes through the choroidal fissure → temporal horn of LV Vascular territory:
- Choroid of the LVs (especially in the lateral horn) Hippocampus, amygdala, uncus
- Globus pallidus, caudate tail, putamen Thalamus (VL)
- IC (posterior limb and retrolenticular)
- Optic tract, lateral geniculate nucleus, optic radiation
- Historically, this artery was sacrificed to treat Parkinson’s disease: decreased tremor likely due to decreased blood supply to VL thalamus.
Posterior Choroidal arteries (medial and lateral)
Medial Posterior Choroidal Artery
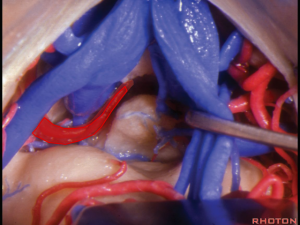
- Medial branches supply pineal gland, tectum, thalamus, choroid of the third ventricle
- Usually arise from the proximal P2 of the PCA
- הולך אחורה בציסטרנה אמביאנס
- בהמשך מסתובב קדימה לתוך גג החדר השלישי
Lateral Posterior Choroidal Artery
- Lateral branches enter the choroidal fissure and anastomose with the anterior choroidal arteries forming variable anastomotic network