Malformations of Cortical Development: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "Categorized into three groups: {| class="wikitable" |- ! Group !! Characteristics !! Conditions |- | Group I || Malformations resulting from abnormal proliferation of neuronal and glial cells || Microcephaly, macrocephaly, FCDs without and with balloon cells (Taylor dysplasia types IIa and IIb), hemimegalencephaly, tuberous sclerosis, dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors (DNETs), gangliogliomas, gangliocytomas |- | Group II || Malformations resulting from abnormal neu...") |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Categories = | |||
* group I: abnormal cell proliferation or apoptosis | |||
* group II: abnormal neuronal migration | |||
* group III: abnormal cortical organization | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Group !! Characteristics !! Conditions | ! Group !! Characteristics !! Conditions | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Group I || | | Group I || abnormal proliferation of neuronal and glial cells || | ||
* Microcephaly | |||
* macrocephaly | |||
* FCDs without and with balloon cells (Taylor dysplasia types IIa and IIb), | |||
* hemimegalencephaly, | |||
* tuberous sclerosis, | |||
* dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors (DNETs), gangliogliomas, gangliocytomas | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Group II || | | Group II || abnormal neuronal migration || | ||
* Lissencephaly | |||
* Band Heterotopia | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Group III || | | Group III || abnormal cortical organization || | ||
* Polymicrogyria, | |||
* schizencephaly, | |||
* type I FCDs, | |||
* mild MCDs | |||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Group | |||
! Affected step of development | |||
! MCDs resulting from the disturbance | |||
! Short definition of the MCD | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="4" | Group I | |||
| rowspan="4" | Progenitor cell proliferation and apoptosis | |||
| Microcephaly | |||
| Abnormally small head and brain | |||
|- | |||
| Macrocephaly | |||
| Abnormally big head and brain | |||
|- | |||
| Hemimegalencephaly | |||
| Overgrowth of (part of) a cerebral hemisphere | |||
|- | |||
| Focal cortical dysplasia | |||
| Disturbed lamination and dysmorphic neurons | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="3" | Group II | |||
| rowspan="3" | Neuronal migration | |||
| Lissencephaly type I | |||
| Absence of normal convolutions/folds | |||
|- | |||
| Periventricular heterotopia (PH) | |||
| Neurons accumulating at the ventricles underneath a normal cortex | |||
|- | |||
| Subcortical band heterotopia/double cortex | |||
| Band of grey matter located between the lateral ventricular wall and the cortex | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="3" | Group III | |||
| rowspan="3" | Neuronal organisation | |||
| Cobblestone lissencephaly/lissencephaly type II | |||
| Overmigration of neurons to localize on the surface of a brain with reduced gyri | |||
|- | |||
| Polymicrogyria | |||
| Too many (usually small) folds/convolutions | |||
|- | |||
| Schizencephaly | |||
| Fluid-filled cleft from ventricle(s) to pia lined by heterotopic grey matter | |||
|} | |||
= Group II - Neuronal migration disorders = | |||
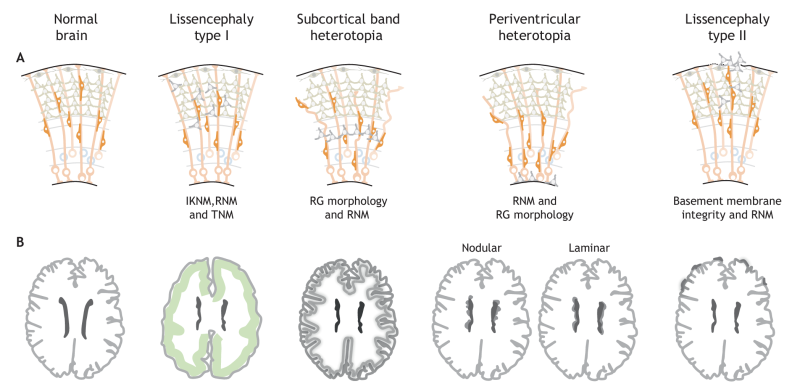
[[File:Cellular and morphological defects associated with neuronal migration disorders.png|center|frameless|800x800px|(A) Schematics highlighting the cellular basis of NMDs in the adult human cortex, showing the different cortical layers and neuronal migrations. Single ectopic neurons are shown in grey and the affected structures or processes are indicated. (B) Schematic showing the MRI-detectable morphological defects in the adult human brain that are caused by the cellular defects of each NMD. Ectopically located clusters of affected neurons are shown as greyshading. Lissencephaly type I is characterized bya smooth brain surface and a simplified fourlayered cortex (indicated by green shading). In subcortical band heterotopia, the cortex contains an additional band of grey matter underneath the white matter. Periventricular heterotopia is characterized by clusters (nodular) or sheets (laminar) of neurons accumulating at the ventricles underneath a normal cortex. In lissencephaly type II, neuronsovermigrate ontothecorticalsurface. Schematicsareadapted fromMRIimages,seee.g.BizzottoandFrancis,2015;Francisetal., 2006; Guerrini and Parrini, 2010. IKNM, interkinetic nuclear migration; RG, radial glia; RNM, radial neuronal migration; TNM, tangential neuronal migration.]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:07, 22 May 2024
Categories
- group I: abnormal cell proliferation or apoptosis
- group II: abnormal neuronal migration
- group III: abnormal cortical organization
| Group | Characteristics | Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Group I | abnormal proliferation of neuronal and glial cells |
|
| Group II | abnormal neuronal migration |
|
| Group III | abnormal cortical organization |
|
| Group | Affected step of development | MCDs resulting from the disturbance | Short definition of the MCD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group I | Progenitor cell proliferation and apoptosis | Microcephaly | Abnormally small head and brain |
| Macrocephaly | Abnormally big head and brain | ||
| Hemimegalencephaly | Overgrowth of (part of) a cerebral hemisphere | ||
| Focal cortical dysplasia | Disturbed lamination and dysmorphic neurons | ||
| Group II | Neuronal migration | Lissencephaly type I | Absence of normal convolutions/folds |
| Periventricular heterotopia (PH) | Neurons accumulating at the ventricles underneath a normal cortex | ||
| Subcortical band heterotopia/double cortex | Band of grey matter located between the lateral ventricular wall and the cortex | ||
| Group III | Neuronal organisation | Cobblestone lissencephaly/lissencephaly type II | Overmigration of neurons to localize on the surface of a brain with reduced gyri |
| Polymicrogyria | Too many (usually small) folds/convolutions | ||
| Schizencephaly | Fluid-filled cleft from ventricle(s) to pia lined by heterotopic grey matter |
Group II - Neuronal migration disorders